Professor Lee Ho-jun's research team in the Department of Artificial Intelligence develops ...
- Writer :External Affairs Team
- Date :2025.05.07
- Views :299
Professor Lee Ho-jun's research team in the Department of Artificial Intelligence develops a solution to the order bias of graph neural networks
- Development of a method to solve the order bias problem of graph neural networks, confirmation of improvement of graph neural networks performance
- Publication of research results in IEEE TNSE (IF=6.7, Top 3.3% in the field) which is the best international academic journal in network science
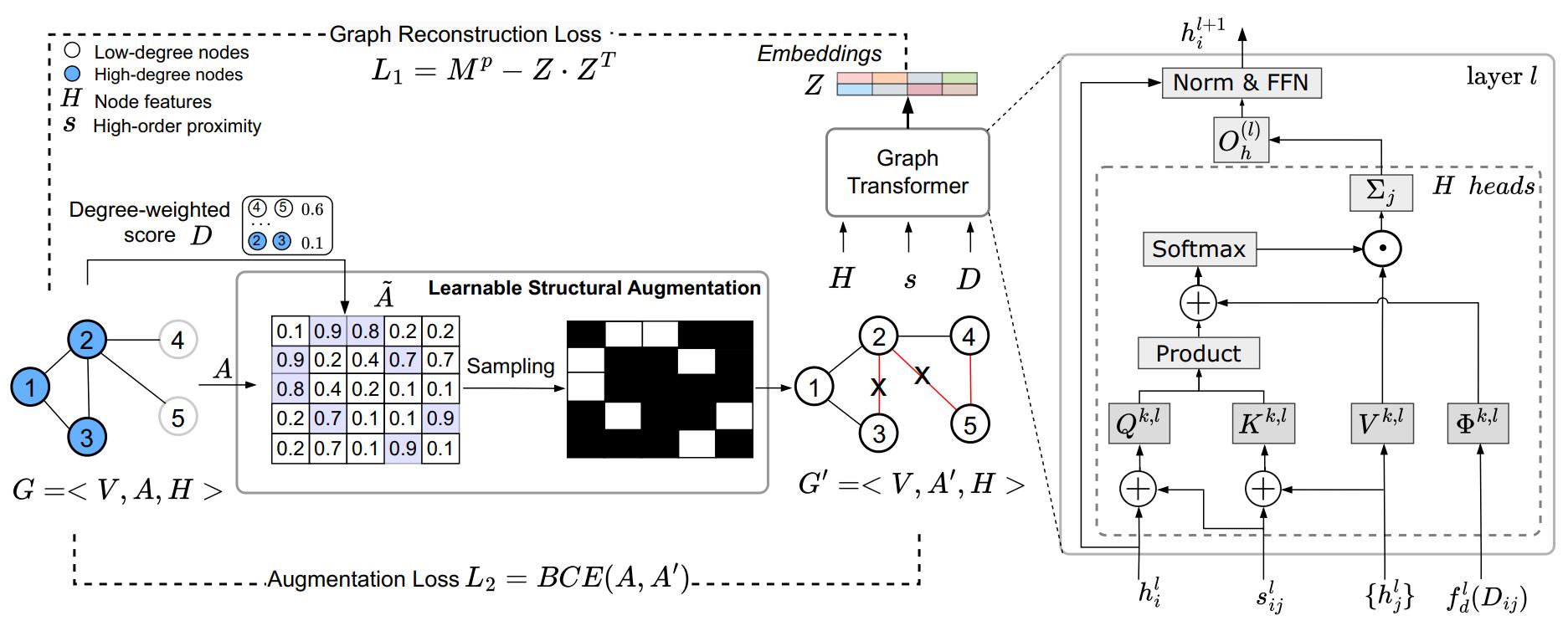
△ An overview of the structure and learnable structural augmentation and structural self-attention mechanisms of the DegFairGT model developed to solve the order bias problem
Professor Lee Ho-joon of The Catholic University of Korea's artificial intelligence department and Dr. Hwang Bantu from the Network Science Lab developed a technology that effectively overcomes the "Degree Bias problem," a representative limitation of graph neural networks (GNNs), through joint research with Hyun-joo Jeon of the Korea Next-Generation Numerical Prediction Model Development Project (KIAPS).
The results of this study were published in IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering (IF=6.7, top 3.3% in the field), the most prestigious international academic journal in network science, and were recognized for their excellence. The Catholic University of Korea's artificial intelligence and network science laboratory was once again recognized for its world-class research capabilities in the field of network science and graph neural networks following AAAI 2024 and AAA1 2025.
Graph neural networks deliver messages based on the principle of homogeneity that connected nodes have similar characteristics. However, in actual graph data, the order distribution is unbalanced, and messages are excessively concentrated on higher-order nodes, and low-order nodes frequently experience order bias problems that degrade their performance due to lack of information.
In response, the research team proposed a "DegFair GT (DegFairness Graph Transformer) model that mitigates order bias by utilizing learnable structural augmentation and structural self-attention mechanisms. This model solves the problem of under-expression of low-order nodes by discovering structural similarities between non-connected nodes and delivering additional messages to low-order nodes. In addition, it eliminates connections with low structural similarities to alleviate the problem of over-expression of higher-order nodes.
The core of the DegFairGT model is to actively learn structural similarities between unconnected nodes performing the same role and to aggregate messages containing additional useful information while maintaining existing connection relationships. In addition, to maintain the stability of the graph structure, a normalization method based on reconstructing the probability of information transition between nodes was introduced to minimize noise messages generated during the structural augmentation process.
As a result of the experiments, the proposed DegFairGT model showed superior results in order bias mitigation, node classification, and node clustering performance compared to existing state-of-the-art methods in various experiments using six datasets. This proves that it is a method that can fundamentally improve the order bias problem and improve the performance of graph neural networks in a balanced way.
"The aberration bias is a major challenge common in most real-world graph data," said Lee Ho-joon, a professor of artificial intelligence at The Catholic University of Korea. "This study is expected to greatly contribute to the spread and commercialization of graph neural network technology."

