-
The CUK College of Medicine’s Research Team, Led by Professor Cho Mila, Was the First to Discover a Novel Cytokine ImmuAuthor : 관리자Date : 2023.01.13Hit : 363
-
- Confirmed the effect of p40-EB13 conjugates by suppressing Th17, pathogenic lymphocytes, and inducing Treg cells, which regulate immune responses
- Confirmed the effect of p40-EB13 conjugated proteins on immune T cell regulation
- Proved the novel heterodimeric cytokine consisting of p40 and EB13 for the first time

Professor Cho Mila Cho and Doctor Lee Sunyoung from the College of Medicine
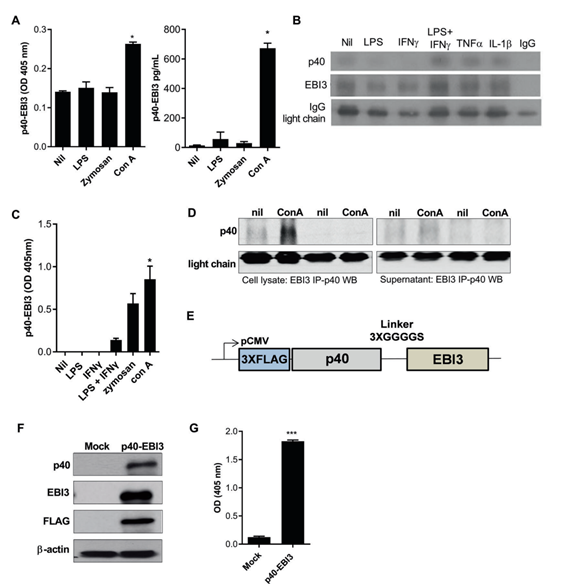
The research team led by Professor Cho Mila and Doctor Lee Sunyoung at the Catholic University of Korea's Department of Biomedicine & Health Science, College of Medicine, established the existence of a cytokine composed of p40 and EB13, conjugated proteins that can control immune T cells, to suggest a new treatment method and potential applications for intractable autoimmune disorders.
Professor Cho’s research team hypothesized the presence of a p40-EBI3 heterodimer in an animal model and investigated its role in immune response regulation. The Interleukin (IL)-12 cytokine family is related to T cells that activate or suppress autoimmune disorders, while IL-12 family members, in general, are heterodimers that share three α units, ""p35, p19, and p28"" as well as two β units, ""p40 and EBI3."" However, there is a homodimer of P40 in the β unit, which inhibits the delivery of IL-23 signaling in inflammation. As a result, the research team assumed the presence of p40-EBI3 heterodimer in the β unit and identified its role in regulating immune responses. The research team confirmed the expression of p40-EBI3 in dendritic cells and demonstrated that it can treat rheumatoid arthritis, an intractable autoimmune disorder, by activating and promoting cytodifferentiation of Treg cells, which can regulate immune responses.
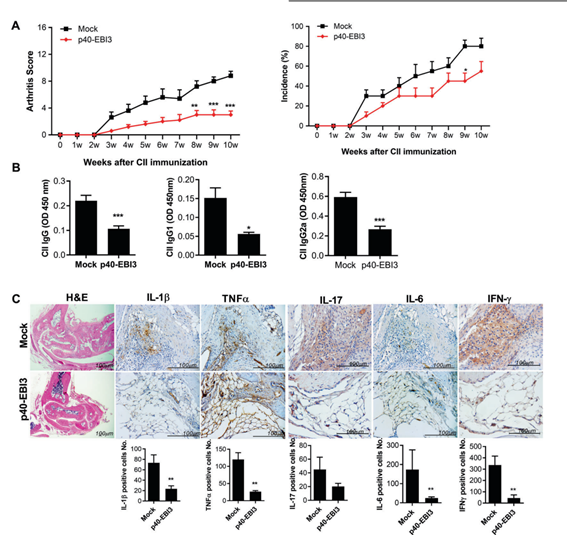
The researchers confirmed the presence of a p40-EBI3 heterodimer in vivo and were able to activate rheumatoid arthritis by injecting a p40-EBI3 gene, protein p40-EBI3 gene, and proteins while suppressing the activation of immune cells expressing the inflammatory cytokine, ""L-17, IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α."" In addition, it was found that the p40-EBI3-Fc protein in vitro significantly inhibited the cytodifferentiation of Th17 cells while increasing the activation of CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ regulating Treg cells.
In other words, the study discovered that p40-EBI3 improves Rheumatoid Arthritis symptoms and inflammation in vivo and in vitro. Thus, the research team suggested that p40-EBI3 is a novel anti-inflammatory cytokine involved in suppressing immune responses by increasing Treg cells while suppressing Th17 cells and osteoclast formation.
The previous study by the research team has reported that inducing the increase of Treg cells that plays an important role in repressing Th17 cells that expresses IL-17 inflammatory cytokines and, at the same time, in immune homeostasis in tackling chronic inflammatory arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis.
Pathogenic Th17 cells and regulating Treg cells can be selectively differentiated and developed by controlling the activation of their respective transcription factors, STAT3 and STAT5, whereas the p40-EBI3 protein promotes the activation of regulating Treg cells in immune T cells by activating the STAT5 transcription factor.
As a result, the researchers demonstrated the immune response regulation effect of p40-EBI3-Fc proteins in rheumatoid arthritis and proposed a new cure as well as potential applications for intractable autoimmune disorders.
“I feel rewarded that I was able to confirm that p40-EBI3 conjugated protein was found to have a mechanism to induce immune regulation, thus immune homeostasis, whereas most drugs in the existing autoimmune disease drug market were developed with an emphasis on suppressing immune responses,” said Prof. Cho Mila, “I intend to register the novel cytokine of p40-EBL3 conjugate protein and complete the development of a drug based on it to help patients who are suffering from an absence of immune regulation drugs.”
Meanwhile, the study was recently published in one of the world's most prestigious journals, "Cell Mol Immunol (IF 22.096)," under the title "A novel cytokine consisting of the p40 and EBI3 subunits suppresses experimental autoimmune arthritis via reciprocal regulation of Th17 and Treg cells."

-
Attachment File

